Understanding the Difference Between DC and AC: A Simple Guide
If you've ever wondered about the different types of electricity powering your home and devices, you're in the right place. Let’s dive into the basics of Direct Current (DC) and Alternating Current (AC), and why both are essential in our world.
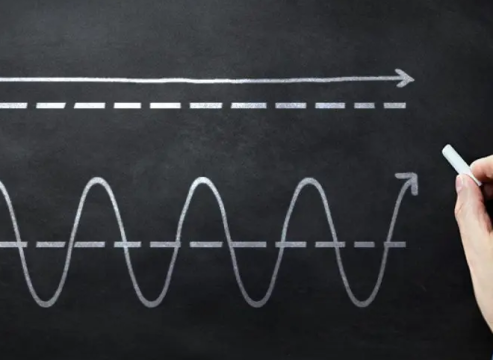
What is Direct Current (DC)?
Direct Current (DC) is the type of electrical current where the flow of electric charge is in one constant direction. It’s like water flowing through a pipe straight to its destination. Batteries, solar panels, and most electronics use DC power because it provides a stable and continuous flow of electricity.
Examples of DC power sources:
Batteries (like those in your phone or car)
Solar panels
Laptop adapters
What is Alternating Current (AC)?
Alternating Current (AC) is the type of electrical current where the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction. Imagine water sloshing back and forth in a pipe. This current changes direction many times per second, which makes it very efficient for transmitting over long distances.
Examples of AC power sources:
The electrical outlets in your home
Large-scale power plants
Most household appliances
Why Do We Use Both DC and AC?
The use of both DC and AC is all about efficiency and practicality:
Transmission Efficiency: AC is much more efficient at transmitting electricity over long distances. This is why our electrical grid uses AC to deliver power from power plants to homes and businesses. DC, on the other hand, is better for short distances and lower voltage applications.
Energy Conversion: Many modern devices require DC power to operate. While the electricity from the grid is delivered as AC, devices like computers and smartphones convert it to DC. This conversion is handled by adapters and power supplies.
Different Applications: Some applications require the stable, constant flow of DC, while others benefit from the variable nature of AC. For instance, AC is used in motors and transformers where the ability to change voltage levels efficiently is crucial.
Understanding the Converter’s Role
In our modern world, devices that use DC power often rely on converters to change AC from the grid into DC. These converters ensure your devices get the right type of power for their needs.
Conclusion
Grasping the difference between DC and AC is fundamental for understanding how our electric-powered world operates. Each type of current plays a unique and vital role in our daily lives, from the power plants generating electricity to the gadgets in our pockets.

